Module 8: Chapter 8: Gases
Section outline
-
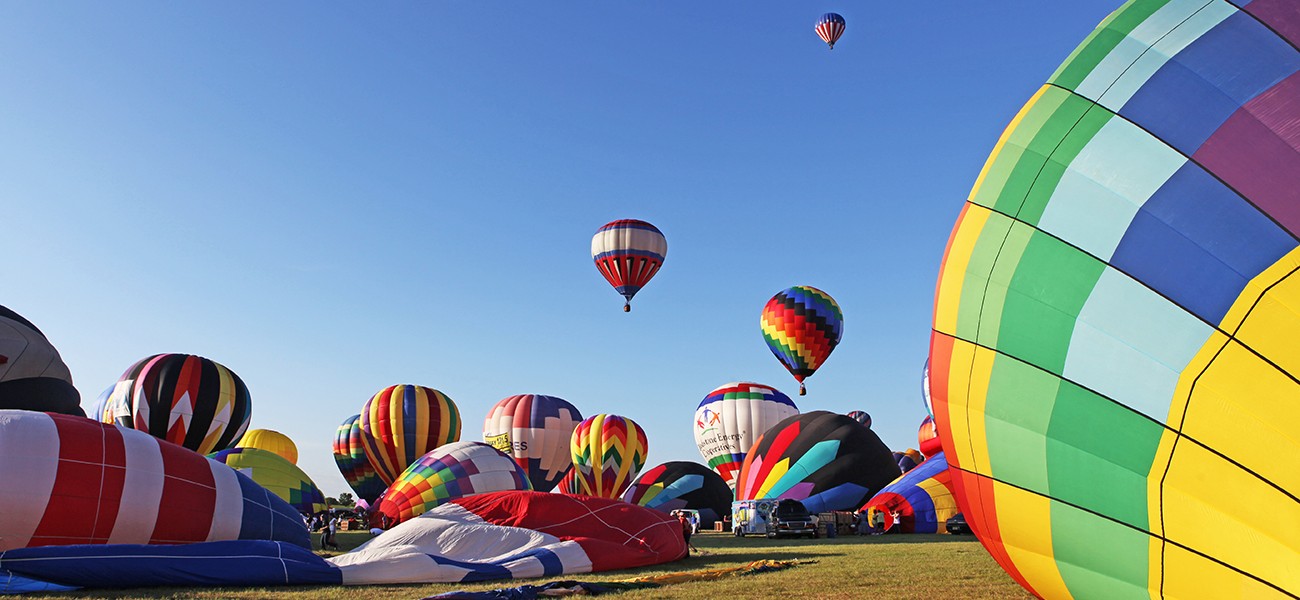

Figure 8.1 The hot air inside these balloons is less dense than the surrounding cool air. This results in a buoyant force that causes the balloons to rise when their guy lines are untied. By: Rice University Openstax CC BY NC SA
Chapter Outline
- Gas Pressure
- Relating Pressure, Volume, Amount, and Temperature: The Ideal Gas Law
- Stoichiometry of Gaseous Substances, Mixtures, and Reactions
- Effusion and Diffusion of Gases
- The Kinetic-Molecular Theory
- Non-Ideal Gas Behavior
Upon completion of this module, you will be able to:
Gas Pressure (8.1)- Define the property of pressure (CLO1)(CLO3)
- Define and convert among the units of pressure measurements (CLO1)(CLO2)
- Describe the operation of common tools for measuring gas pressure (CLO1)
- Calculate pressure from manometer data (CLO2)
Relating Pressure, Volume, Amount, and Temperature: The Ideal Gas Law (8.2)
- Identify the mathematical relationships between the various properties of gases (CLO1)(CLO2)
- Use the ideal gas law, and related gas laws, to compute the values of various gas properties under specified conditions (CLO1)(CLO2)
Stoichiometry of Gaseous Substances, Mixtures, and Reactions (8.3)- Use the ideal gas law to compute gas densities and molar masses (CLO2)
- Perform stoichiometric calculations involving gaseous substances (CLO2)
- State Dalton’s law of partial pressures and use it in calculations involving gaseous mixtures (CLO1)(CLO2)
Effusion and Diffusion of Gases (8.4)
- Define and explain effusion and diffusion (CLO1)
- State Graham’s law and use it to compute relevant gas properties (CLO1)(CLO2)
The Kinetic-Molecular Theory (8.5)
- State the postulates of the kinetic-molecular theory (CLO1)
- Use this theory’s postulates to explain the gas laws (CLO1)
Non-Ideal Gas Behavior (8.6)
- Describe the physical factors that lead to deviations from ideal gas behavior (CLO1)
- Explain how these factors are represented in the van der Waals equation (CLO1)
- Define compressibility (Z) and describe how its variation with pressure reflects non-ideal behavior (CLO1)
- Quantify non-ideal behavior by comparing computations of gas properties using the ideal gas law and the van der Waals equation (CLO1)(CLO2)
To achieve these objectives:
- Read and view the Module 8: Chapter 8: Gases in Moodle
- Read Chapter 8: Gases in the OpenStax Chemistry: Atoms First 2e Pressbook
- Complete the Module 8: Chapter 8: Gases Assignment
- Complete the Module 8: Chapter 8: Gases Discussion
- Complete the Module 8: Lab 8: Video (VWS) Assignment - Kinetic Molecular Theory of Gases
- Complete the Module 8: Lab 8: Experiment - Gas Laws
- Complete the Module 8: Lab 8: Report Assignment - Gas Laws
Module Pressbooks Resources and Activities
You will find the following resources and activities in this module at the Pressbooks website. Click on the links below to access or complete each item.
Background Colour
Font Face
Font Kerning
Font Size
Image Visibility
Letter Spacing
Line Height
Link Highlight
Text Colour