Module 5: Cell Structure & Function
Section outline
-
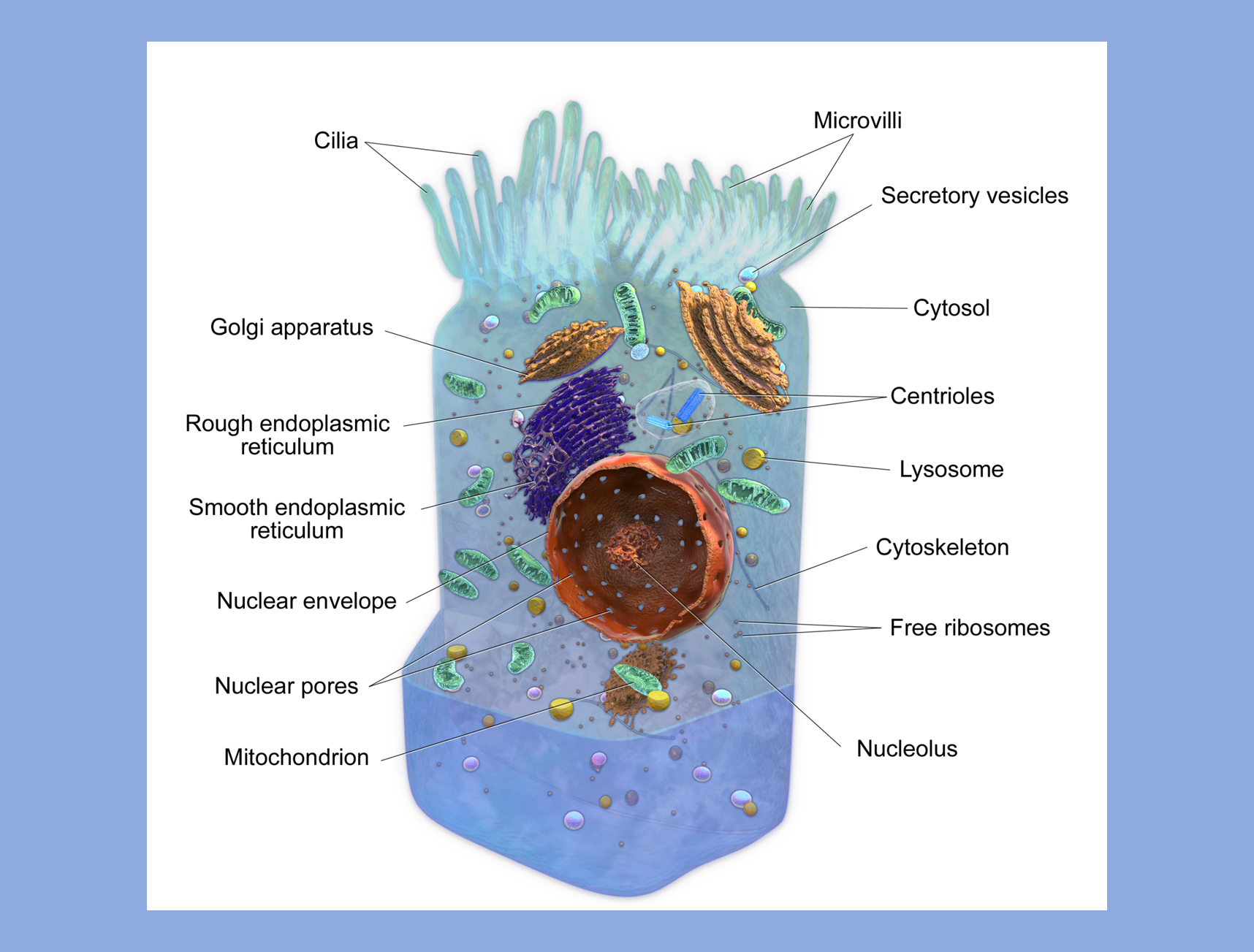
The purpose of this guide is to provide an overview of the basic structural components of living cells and their functions. Although our body is composed of chemicals, the smallest structural and functional unit of life begins with the cell. An average human body contains approximately 37.2 trillion (37,200,000,000,000) cells. The cells in the human body are active; they grow, specialize, and function, and most of them repair, reproduce, and die. There are 226 different kinds of cells in the human body. Most of our body cells have three main parts: the (plasma)cell membrane, which protects the integrity of the cell aside from other functions; the nucleus, which carries the hereditary material in the form of DNA; and the cytoplasm, gelatinous liquid with the suspended organelles that fills the area between the nucleus and the cell membrane. Each type of cytoplasmic organelle has a definite structure and a specific role in the function of the specific type of cell. Cytoplasmic organelles include mitochondria, ribosomes, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, vesicles, peroxisomes, and lysosomes. Understanding the structure of cells is one of the first steps in comprehending the complex cellular interactions that direct and produce life.
Upon completion of this module, you will be able to:- Specify the characteristics associated with life and explain why the cell is the basic unit of life. (C.L.O #2 and #3)
- Describe the levels of structural organization in the body. (C.L.O #2 and #3)
- Describe the structure and the functions of the major components of a cell. (C.L.O. #2, #3, and #4)
- Define metabolism and distinguish between anabolism and catabolism. (C.L.O. #1 and #3)
- Describe the cellular processes involved in the growth of the human body from a fertilized egg to an adult. (CLO #1 and #4)
- Explain the importance of cell differentiation to an organism. (C.L.O. #2 and #3)
- Describe the general characteristics of each of the following cell types and relate their characteristics to their functions: nerve cell, muscle cell, red blood cell (erythrocyte), and white blood cell (leukocyte). (C.L.O. #1, #3, and #4)
To achieve these objectives:
- Read the Module 5 Introduction. (C.L.O #1, C.L.O.#4)
- Read Chapter 6 in the textbook. (C.L.O #1, C.L.O. #4)
- Test Your Knowledge sections are located at the end of each segment in the chapter. Answering the questions in these sections will aid in your knowledge to help you with the course. These questions will be relevant for information on testing and quizzes. (C.L.O. #1, C.L.O. #2, C.L.O. #4)(M.L.O. #1, M.L.O. #2, M.L.O. #3, M.L.O. #4, M.L.O. #5, M.L.O. #6, M.L.O. #7)
- Complete the exercises in the "Practice" section at the end of the chapter. (C.L.O. #1, C.L.O. #2)(M.L.O. #1, M.L.O. #2, M.L.O. #3, M.L.O. #4, M.L.O. #5, M.L.O. #6, M.L.O. #7)
- Complete the discussion activity. (C.L.O #1 and #4), (M.L.O. #1)
- Complete the quiz.(C.L.O. #1, C.L.O. #2, C.L.O. #3, C.L.O. #4)(M.L.O. #1, M.L.O. #2, M.L.O. #3, M.L.O. #4, M.L.O. #5, M.L.O. #6, M.L.O. #7)
Module Pressbooks Resources and Activities
You will find the following resources and activities in this module at the Pressbooks website. Click on the links below to access or complete each item.
-
Read chapter, review the "Test Your Knowledge" questions, and complete the activities in the "Practice" section at the end of the chapter.
-
This quiz will have 10 questions. It is worth 20 points. You are allowed two attempts at this quiz. Correct answers will be available for review after the quiz is closed.
Directions for Instructors: Load questions from the Module 5 Question Bank.Set close date and then tick "Right answer" box under "After the quiz is closed" section of Review Options.
Background Colour
Font Face
Font Kerning
Font Size
Image Visibility
Letter Spacing
Line Height
Link Highlight
Text Colour