Module 4: Discrete Random Variables (Chapter 4)
Section outline
-
 Let us begin with two different examples of the types of probability problems we'll be able to model using the techniques of this chapter.
Let us begin with two different examples of the types of probability problems we'll be able to model using the techniques of this chapter.Example 1: Suppose a student takes a ten-question, true-false quiz. Because the student had such a busy schedule, they could not study and guess randomly at each answer. What is the probability of the student passing the quiz with at least a 70%?
Example 2: Small companies might be interested in the number of unread emails sitting in their employee's mailboxes. If the average number of unread emails is 100 at the end of the workday, what is the probability that on a given day, the employees have more than 120 unread emails at the end of the workday?
Each of these probabilities can be found if we know the distribution of the corresponding discrete random variable. Recall that discrete data are data that you can count. A random variable describes the outcomes of a statistical experiment in words. The values of a random variable can vary with each repetition of an experiment.
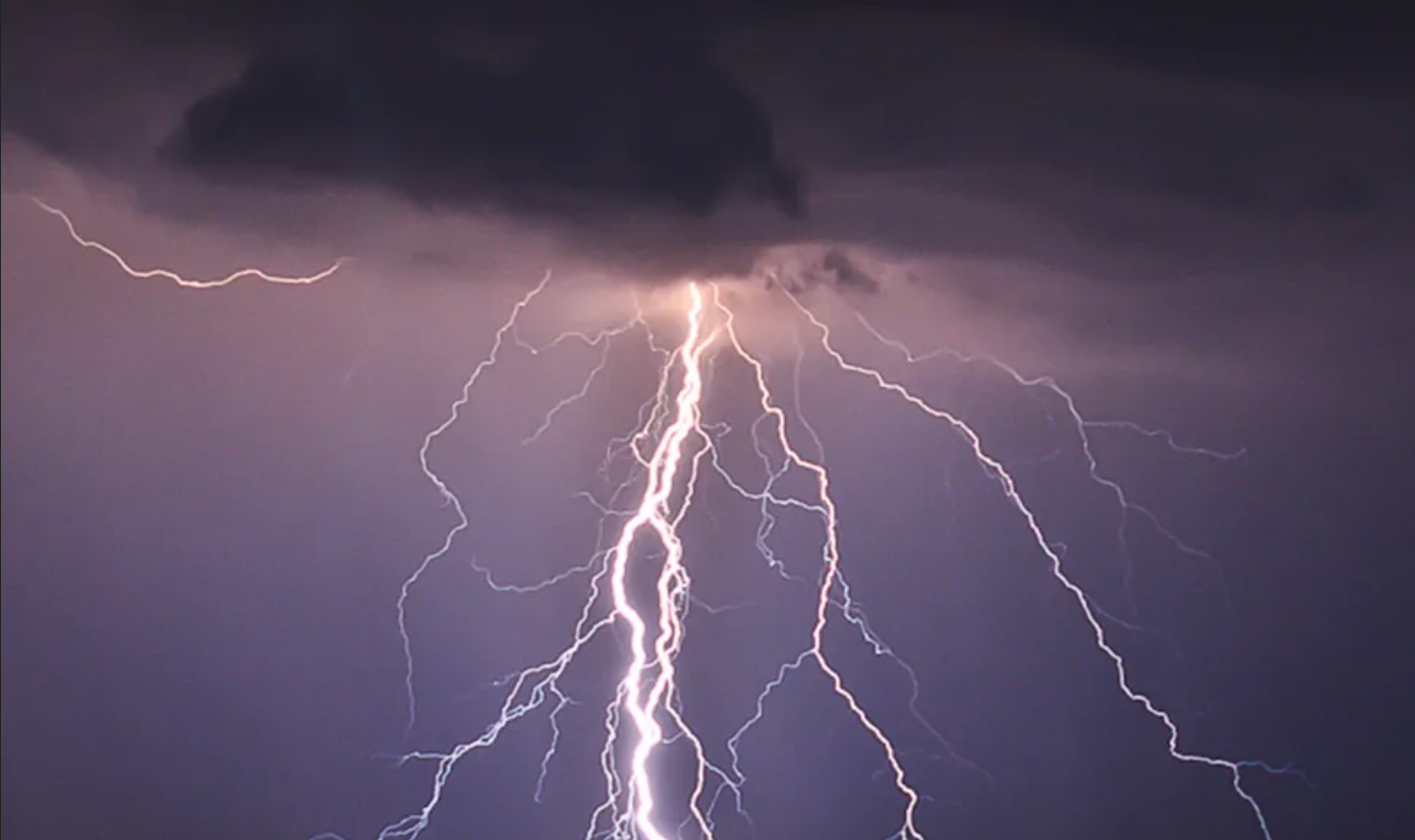
Image Caption: You can use probability and discrete random variables to calculate the likelihood of lightning striking the ground five times during a half-hour thunderstorm. (Credit: Leszek Leszczynski)
(Content & Image Source: Chapter 4 Introduction, Introductory Statistics, Barbara Illowsky and Susan Dean, OpenStax, CC BY 4.0 License)
Upon completion of this module, you will be able to:4.1 Probability Distribution Function (PDF) for a Discrete Random Variable- Validate the properties of a discrete probability distribution function
- Write a probability distribution function for given discrete data
4.2 Measures of General Discrete Random Variables- Calculate and interpret expected values of general random variables
- Calculate and interpret the variance and standard deviation of general random variables
4.3 Binomial Distribution- Identify the components of a binomial experiment
- Use the formulas for a binomial random variable to compute mean, variance, and standard deviation
4.4 Geometric Distribution- Identify the components of a geometric experiment
- Use the formulas for a geometric random variable to compute mean, variance, and standard deviation
4.5 Hypergeometric Distribution- Identify the components of a hypergeometric experiment
- Use the formulas for a hypergeometric random variable to compute mean, variance, and standard deviation
4.6 Poisson Distribution- Identify the components of a Poisson experiment
- Use the formulas for a Poisson random variable to compute the mean, variance, and standard deviation
To achieve these objectives:- Read the Module 4 Introduction (see above).
- Read Sections 4.1 - 4.6 of Chapter 4: Discrete Random Variables in Introductory Statistics (links to each Section provided below)
- Complete the MyOpenMath Homework Assignments for the topics in the Chapter (links provided below) - These are graded!
- View the Chapter 4 Review (link provided below)
- Practice the problems in the Chapter 4 Practice and Homework, checking the solutions provided (links to each provided below)
- Submit the Chapter 4 Project I: Lucky Dice Experiment or the Chapter 4 Project II: Playing Card Experiment (links to project and submission link provided below)
- Complete the MyOpenMath Quiz for Chapter 4 (link provided below) - This is graded!
- Once you complete the Quiz, upload your work in the Quiz Work Upload Assignment using the submission link below.
- Post in the Chapter 4 Q&A Discussion Forum - link provided below.
Note the check boxes to the right that help you track your progress: some are automatic, and some are manual.Module Pressbooks Resources and Activities
You will find the following resources and activities in this module at the Pressbooks website. Click on the links below to access or complete each item.
Background Colour
Font Face
Font Kerning
Font Size
Image Visibility
Letter Spacing
Line Height
Link Highlight
Text Colour