Module 9: Chapter 9: Electricity and Electrical Circuits
Section outline
-
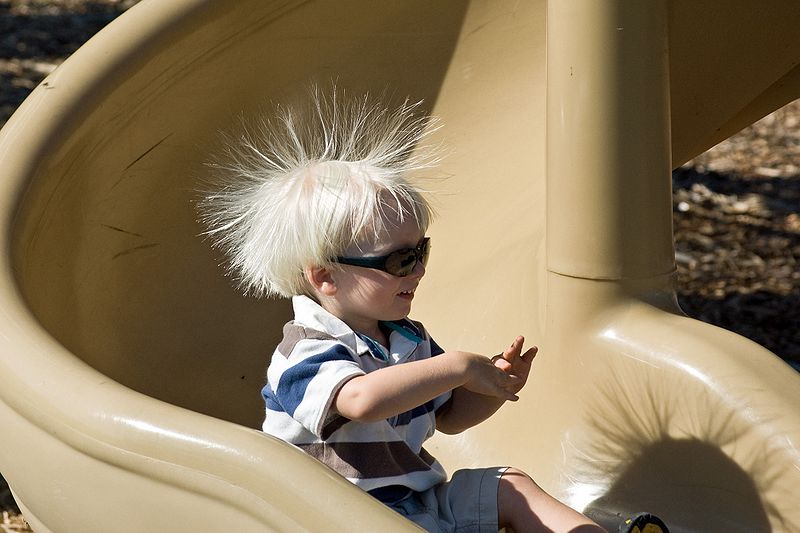

Figure 9.1 Fig. 9.1 Static electricity from this plastic slide causes the child’s hair to stand on end. The sliding motion stripped electrons away from the child’s body, leaving an excess of positive charges, which repel each other along each strand of hair. (credit:)Chapter Outline
- Introduction to Electricity
- Static Electricity and Conservation of Charge
- Charge Carried by Electrons and Protons
- Separation of Charges in Atoms
- Coulomb's Law
- Electric Field and Electric Forces
- Electric Current and Electric Circuitry
- Ohm's Law
- Resistance and Simple Circuits
- Resistors in Parallel and In Series
- Direct Current and Alternating Current
- Voltmeters and Ammeters
Upon completion of this module, you will be able to:
- Define: static electricity (CLO2)(CLO3)
- Determine the type of electric charge present (CLO2)(CLO3)(CLO4)
- State units of charge and electric force in SI units. (CLO2)(CLO5)
- Explain various electrostatic interactions (CLO2)(CLO3)
- Define: electrical force, and electric field (CLO2)
- State Coulomb’s Law (CLO1)(CLO2)
- Discuss the relationships between the variables in Coulomb’s Law equation. (CLO2)(CLO3)(CLO5)
- Describe interactions between charges and electric fields. (CLO2)(CLO3)
- Use Coulomb’s Law to calculate electric force (CLO5)
- Compare the Coulomb Force to the Gravitational Force (CLO2)(CLO3)(CLO5)
- Define electric current, electric resistance, and voltage. (CLO2)(CLO3)
- State Ohm’s Law. (CLO1)
- Use the correct units of current, voltage, and resistance in the metric systems. (CLO5)
- Explain the relationships between the variables in the Ohm’s Law formula (CLO2)(CLO3)
- Use Ohm’s Law to solve simple circuit problems (CLO5)
- Determine the electric resistance, voltage, electric current, and power in a circuit (CLO2)(CLO3)(CLO5)
- Discuss the relationship between energy, power, voltage, current, and resistance in a circuit. (CLO2)(CLO3)
- Describe and differentiate between parallel and series electrical circuits. (CLO2)(CLO3)
- Determine the equivalent resistance for series and parallel combinations of resistors. (CLO2)(CLO5)
- Determine the frequency, electric resistance, voltage, and electric current in a simple AC circuit (CLO2)(CLO3)(CLO5)
-
Explain the function of a coil, resistor, and capacitor in a circuit (CLO2)(CLO3)
To achieve these objectives:
- Read and view the Module 9: Chapter 9: Electricity and Electrical Circuits in Moodle
- Read Chapter 9: Electricity and Electrical Circuits in the Exploring the Physical World Introductory Chemistry and Physics Pressbook
- Complete Module 9: Chapter 9: Electricity and Electrical Circuits Assignment
- Complete Module 9: Chapter 9: Electricity and Electrical Circuits Discussion
- Complete the Module 9: Video (VWS) Assignment - Electricity and Electrical Circuits
- Complete the Module 9: Activity Assignment - Electricity & Electrical Circuits
- Complete the Module 9: Report Assignment - Electricity & Electrical Circuits
Module Pressbooks Resources and Activities
You will find the following resources and activities in this module at the Pressbooks website. Click on the links below to access or complete each item.
-
Opened: Wednesday, October 25, 2023, 8:07 AMDue: Wednesday, November 1, 2023, 8:07 AM
-
Opened: Wednesday, October 25, 2023, 8:07 AMDue: Wednesday, November 1, 2023, 8:07 AM
Background Colour
Font Face
Font Kerning
Font Size
Image Visibility
Letter Spacing
Line Height
Link Highlight
Text Colour